 |
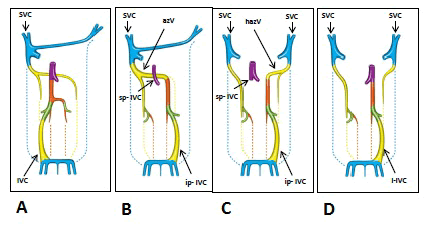
| Figure 1: Embryonal development of the superior and inferior vena cava - normally and in cases of left and right isomerism (drawings). A) Normally: Development of superior and inferior vena cava (SVC/IVC) on 6 to 8 week of pregnancy. Note the paired cranial and caudal precursor veins: cardinal veins (blue), subcardinal veins (yellow), supracardinal veins (orange), connecting sub-/ supracardinal anastomoses (green). The precursors of the hepatic segment of IVC (violet) are vitelline veins, which also give rise to hepatic veins, portal vein and superior mesenteric vein. B) Left isomerism (e.g. A 612): Single SVC originated from right sided cranial cardinal vein. Note the discontinuity of IVC below its superior part (sp-IVC) respectively hepatic segment (violet) and the left-sided malposition of its inferior part (ip-IVC): prerenal (orange), renal (green), postrenal (yellow) segment and the azygos-vein-continuation (azV). C) Left isomerism (e.g. A 799, A 973, A 1079): Bilateral SVC originated from right and left sided cranial cardinal vein. Note the discontinuity of IVC below its superior part (sp-IVC) respectively hepatic segment (violet) and the left-sided malposition of its inferior part (ip-IVC) - prerenal (orange) renal (green) and postrenal (yellow) segment and the hemiazygos-vein- continuation (hazV). D) Right isomerism (e.g. A 722): Bilateral SVC originated from right and left sided cranial cardinal vein. Note the left-sided malposition of the whole IVC (l-IVC). |